![[Updated] 2024 Approved Perfecting Stability A No-Tripod Guide](https://thmb.techidaily.com/2a9cc8bf4d555df620abafcb570dcc2752e8e2040a84b647ff438519a4be3866.jpg)
"[Updated] 2024 Approved Perfecting Stability A No-Tripod Guide"

Perfecting Stability: A No-Tripod Guide
DIY Tripods| How to Stabilize Your Camera without Buying a Tripod

Richard Bennett
Oct 26, 2023• Proven solutions
When you’re trying to grow a channel on YouTube it can feel like equipment is a barrier, but it shouldn’t be. If you can’t afford a high-end tripod, for example, there are loads of ways to get by without one.
DIY Your Video with Wondershare Filmora
Wondershare Filmora has the best video stabilization tool is your videos have a bad frame or were recorded in dim lights. If a video is shot in bad weather or unfriendly situation where you don’t have all the equipment required for a quality recording, Wondershare Filmora can help you in the background to edit your videos like a pro. And it has all the relevant tools like effects, transitions, background removal, overlays, and background music that could turn your normal video to a professional one.
Here are 3 of our favorite DIY tripods.
DIY smartphone tripod using binder clips or hair clips
You’re a solo operation and your best camera is on your phone. That’s pretty common.
If you have a DSLR then you can set it down on any stable surface while filming yourself, but your phone can’t stand up by itself. It needs something or someone to hold it. Do you just accept that and shoot everything as a selfie?
No. No, you don’t, because there are common household items that can help you out of this problem. For this DIY tripod, you need either 2 binder clips or 2 ‘claw clips’ (also called ‘hair jaws’).
Hold your phone in landscape mode (horizontally, so it’s long rather than tall) and attach clips to the bottom corners. If you are worried about scratching your screen, fold up some paper to place between your clip and your phone.
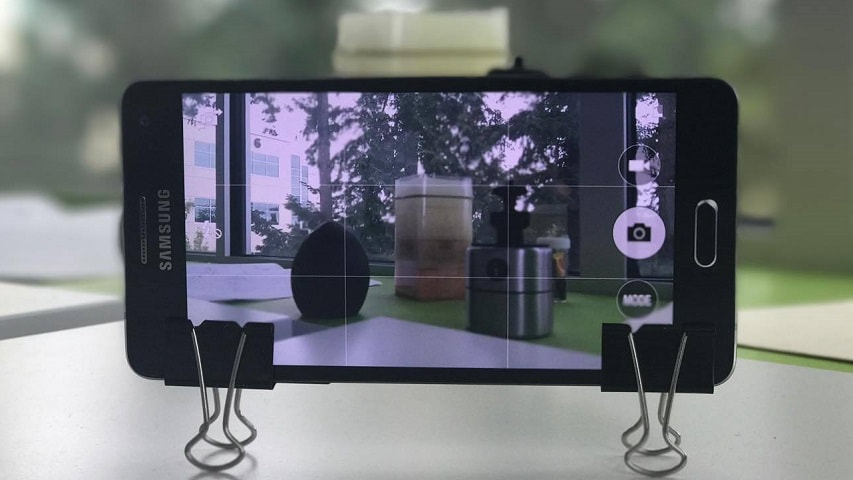
Here it is with binder clips:

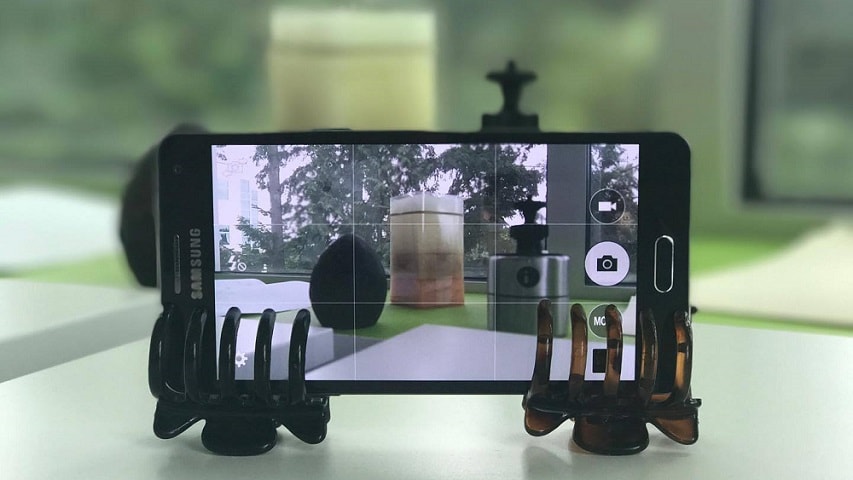
And here it is with hair clips:

Now you can set your smartphone upon any stable surface, like a table or a stack of books.
Here are some more cool ideas!
DIY adjustable tripod using books and a towel
You’ve probably heard a million times that you can stabilize your camera by sitting it down on any stable surface – on your desk, on a stack of books, up in a tree, etc. This is very true!
But if you can use any stable surface, why do people buy tripods?
Because it isn’t convenient to rearrange your furniture whenever you want to make a video, and also because tripods are adjustable. You can change their height, you can use them to pan or tilt, and it’s pretty easy to move them a bit forwards or backward while you’re setting up your shot.
To get similar functions from the ‘any stable surface’ solution you can use a table, a stack of books, and a towel.
- Set up the area where you’re going to sit while you’re filming on one end of the table.
- Put the towel down over the approximate spot you want your camera to be.
- Stack your books on top of the towel.
- Put your camera on top of the books.
Now if your camera isn’t up high enough, or is too high, you can adjust it just by adding or taking away books. If you want to move it closer or farther away from you, just pull the towel forwards or backward.
DIY gripping ‘Gorillapod’ using wire and tape
Gorillapod’s are cool because you can use them like normal tripods, carry them around like selfie sticks, or attach them to things like fences and posts. Here’s how you can make something similar using wire, electrical tape or duct tape, and a 1/4 bolt.
Your wire should be fairly stiff and you’ll need three pieces the same length, which should be at least 10 inches. Old clothes hangers work well. This needs to be something strong enough to support the weight of your camera, but soft enough that it’s not impossible for you to bend.
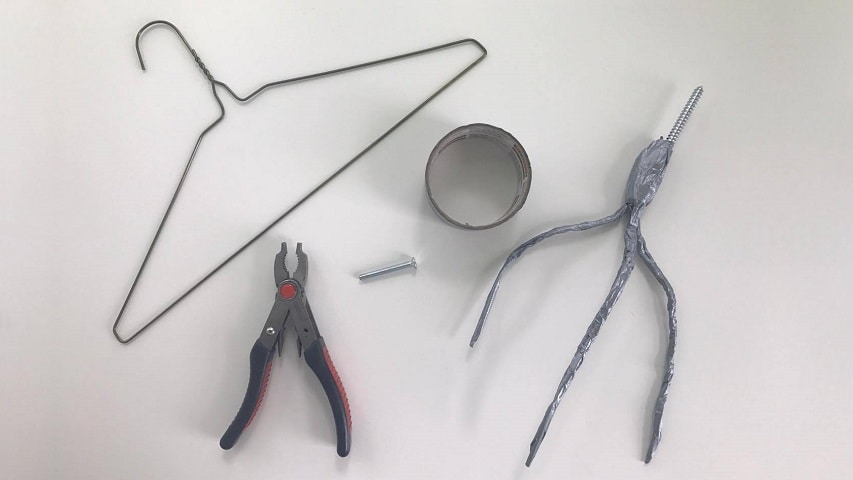

All of your supplies plus the finished product.
Readying your legs
Step 1: Bend 2 inches at one end of each wire into a ‘U’ shape. You will probably need pliers for this.
Step 2: Pick up one of your pieces of wire and wrap one end with electrical tape. Go around 5-10 times (to prevent it from coming undone at the end) and then, without cutting your tape, start moving up and wrapping the rest of your wire. Stop before your ‘U’ section.
Repeat this with the other two wires.
Attaching your legs
Step 1: Place the ‘U’ section of a leg against your bolt. The bolt’s threading should be pointing away from the leg. Now, use your tape to attach them. Wind it around 2 or 3 times, then repeat the process with both of the other legs individually.
Step 2: After all the legs are attached, wrap some more tape around all 3 as tightly as you can.
Your camera will mount onto the bolt! You’ll be able to use this as a normal table-top tripod or use the flexible legs to grab onto different things like a Gorillapod. Read more at Instructables.
Note: make sure the bolt is a fit for your camera before you get too far into this process.

Richard Bennett
Richard Bennett is a writer and a lover of all things video.
Follow @Richard Bennett
Also read:
- [New] In 2024, Leveraging Videos with Text A Cost-Free Approach
- [New] In 2024, Step-By-Step Process Converting YouTube Clips Into Playful GIFs
- [Updated] 2024 Approved The Entrepreneur's Blueprint for Profiting From Video Content
- [Updated] A Beginner's Blueprint Setting Up on YouTube
- [Updated] In 2024, How to Create a Sports YouTube Channel on Mac?
- 2024 Approved Mastering 360-Degree Videos Secure YouTube Uploads
- Enhanced Power User Capabilities with Windows & Sudo
- How to Fix Fall Guys Loading Issues and Avoid Initial Game Crashes
- In 2024, 9 Powerful Methods to Make Money on Your YouTube Shorts
- In 2024, How To Fake GPS On Honor Play 8T For Mobile Legends? | Dr.fone
- In 2024, Mastering Lock Screen Settings How to Enable and Disable on Realme 10T 5G
- Install Newest Targus DisplayLink Software for Windows 11/8/7
- Steps to Unfreeze Spotify on Windows 11 Devices
- Title: [Updated] 2024 Approved Perfecting Stability A No-Tripod Guide
- Author: Jason
- Created at : 2024-11-27 17:42:55
- Updated at : 2024-12-03 22:33:01
- Link: https://youtube-webster.techidaily.com/ed-2024-approved-perfecting-stability-a-no-tripod-guide/
- License: This work is licensed under CC BY-NC-SA 4.0.